reputation-management-1
Patent Review
Skip to - Cellular System Evolution | US Patent Abstract | Invention Disclosed Summary | Topology
Introduction
The deployment of cellular radio system has relied upon the use of radio spectrum in the UHF (300-3000 MHz) or directional radio frequencies to convey bidirectional information between fixed and ambulatory transmitters and receivers. Other directional radio bands SHF (3000-30000MHz) and above are now being developed for the deployment of advanced radio services for even higher speed broadband networks. To deliver 4G or packet based cellular broadband data requires particular types of equipment and deployment which organises the infrastructure to facilitate the reuse of the spectrum available in any area so as to provide broadband over wireless services in urban and suburban environments.
The efficient use of spectrum, whilst complying with the community amenity requirements, has led to a single way to deploy facilities and equipment in any given area in order to deliver radio based broadband data. The determinants governing the capacity and efficiency of bits/Hz over a given area for deployment of such a network are the tower heights, cell radius, system value, data rate, modulation type and spectrum reuse ratio.
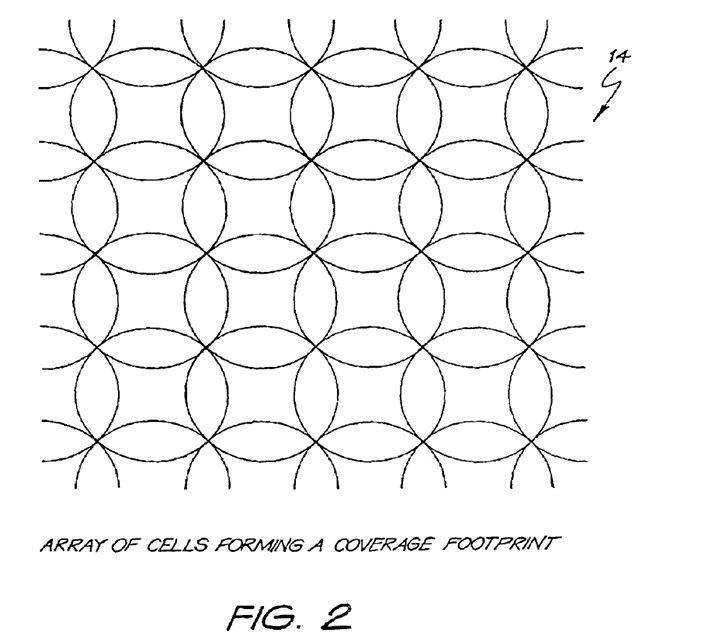
The MICRO WAVE CELLULAR ARCHITECTURE discloses an invention to deliver a radio based broadband network for an area which provides improved capacity of the information (broadband data) delivered in an area and also improves the effective coverage possible as an alternative to building a single very high central tower to service the same area. The tower height of one central tower antenna has been reduced to deal with community impact and to facilitate better coverage by the introduction of multiple lower towers and uses interconnected smaller coverage cells to provide both coverage and reuse of the spectrum in any given area providing a higher coverage ratio and better spectrum efficiency to construct a cellular wireless broadband network.